The Microfinance Market size was valued at USD 185.85 Billion in 2023 and the total Microfinance revenue is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.5% from 2024 to 2030, reaching nearly USD 423.87 Billion in 2030.Microfinance Market Overview
The report covers a detailed analysis of the global microfinance market, including market size, growth prospects, and major players. Also, in-depth examination of the key trends shaping the microfinance sector, such as technological integration, product diversification, social impact investing, and client-centric approaches. The need for financial inclusion is growing, especially in developing nations where a sizable fraction of the populace lacks access to banking. Around 1.4 billion adults worldwide do not have access to traditional banking services, according to the World Bank, which means that microfinance institutions (MFIs) have a huge market opportunity. The demand is being driven by initiatives that support financial inclusion as more individuals become aware of the advantages of formal financial products. Advancements in technology, such as the widespread use of mobile banking and financial technology (fintech), are making unbanked people more accessible, particularly in rural areas. By streamlining loan processing, repayments, and other financial activities, mobile technology lowers expenses and increases reach. Additionally, MFIs' growth is being aided by a favorable regulatory climate that is defined by expedited licensing processes and lowered capital requirements. To meet changing customer needs, MFIs are growing the range of products they offer beyond traditional microloans to include savings accounts, money transfers, insurance, and leasing services. Also, because of the microfinance industry's potential for both financial rewards and social effects, investors are becoming more interested in it, which gives MFIs more funding for service improvement and growth.To know about the Research Methodology :- Request Free Sample Report There are several ways for investors to interact with the microfinance industry. Common ways include participating in microfinance funds that distribute risk across a variety of portfolios, making direct investments in respectable MFIs through stock or debt instruments, or using impact investing platforms that connect investors with social entrepreneurs. Achieving a balance between financial return and effect, doing extensive due diligence on the financial health and governance of MFIs, and adopting a long-term view are all important factors to take into account because sustainable microfinance institution development takes time.
Microfinance Market Dynamics
Financial Inclusion Initiatives Access to savings accounts and loans allows low-income people to invest in education, health, and small companies, thereby breaking the poverty cycle. Financial inclusion promotes entrepreneurship and helps small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs) develop, which in turn fosters economic growth. Broader financial inclusion also improves overall financial stability by lowering reliance on erratic and dangerous unregulated financial channels. The increasing awareness of financial inclusion initiatives and the lowering of obstacles to formal financial services are driving a strong demand for microfinance services. Demand for insurance, savings products, and small loans has increased significantly as more low-income people and SMEs actively look for them. Governments work with microfinance institutions (MFIs) to lower lending risks to underprivileged people by establishing credit bureaus, funding, and favorable legislation that promotes policy. Advancing the spread of microfinance, technology advancements in mobile banking and fintech allow MFIs to reach rural and remote locations at a reasonable cost. The rise of mobile banking and financial technology The rise of mobile banking and financial technology (fintech) presents a transformative opportunity for the microfinance market, particularly in expanding outreach and reducing costs. Mobile technology enables microfinance institutions (MFIs) to reach the unbanked by providing financial services via mobile phones, hence removing the need for physical branches. This improves accessibility, especially for isolated locations or communities without established financial infrastructure. In addition, when compared to conventional branch-based models, mobile solutions significantly cut MFIs' operating expenses, which in turn resulted in reduced borrower interest rates and higher profitability. Also, mobile platforms provide faster loan processing, repayments, and transactions, improving both operational efficiency and client experience. MFIs are expected to improve risk assessment, offer individualized products, and promote financial inclusion by gaining important insights into client behavior and creditworthiness through mobile data analytics. Risk Management Microfinance institutions (MFIs) face numerous risks, including credit, operational, liquidity, and external hazards. Credit risk is increased when serving clients with short credit histories and no traditional collateral, which exacerbates the effects of defaults on the MFI's portfolio and financial stability. Operational risk exposes MFIs to financial losses and reputational damage due to operational issues in remote areas, such as infrastructure limits and potential fraud threats. MFIs that rely on outside finance are vulnerable to funding changes, which are expected to impact loan disbursements and operational costs. It is known as liquidity risk. Additional dangers to operations and market stability include external issues including political unpredictability, economic downturns, and natural disasters. Microfinance institutions (MFIs) face challenges in attracting necessary funds for growth because of increased risks, which has resulted in a loss in investor confidence. Due to their higher risk profiles, MFIs frequently have to charge their clients higher interest rates, which makes it harder for the needy borrowers they are trying to help to receive credit. Inadequate risk management can lead to operational inefficiencies, which impede the ability to scale effectively and affect profitability in general. When the microfinance industry faces high rates of delinquency and systemic concerns, it leads to wider market instability and an economic downturn, which poses difficulties for microfinance institutions (MFIs) and the communities they serve.Microfinance Market Segment Analysis
By Service Type, the Group and Individual Micro Credit segment has the highest market share, by 2023, it account for almost 20%. Microcredit enables low-income individuals and microenterprises by providing credit, ending the cycle of poverty and reliance on high-cost informal lenders. Having access to microloans promotes financial discipline, saves, and eases future financial attempts. Microloans stimulate the growth of microenterprises, resulting in the creation of jobs, revenue, and regional economic development. Also, the growth of microenterprises increases demand for products and services, which promotes the economy's overall growth. Microloans promote the improvement of livelihoods and income growth, allowing people to invest in profitable ventures and improve household well-being. Credit availability promotes long-term social mobility by ending intergenerational cycles of poverty and funding investments in healthcare and education. Individual and group microcredit improve growth and sustainability, draw in a wider clientele, and broaden the microfinance ecosystem. The prosperity of this market draws capital and encourages creativity, which results in the creation of new goods and services that eventually help the microfinance industry as a whole.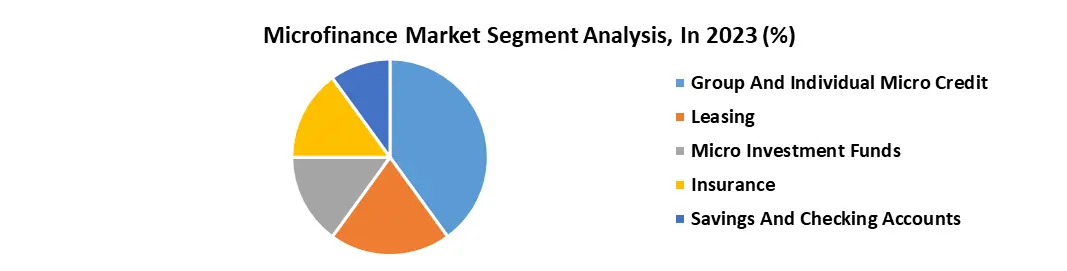
Microfinance Market Regional Analysis
The North America in the microfinance market, demand is increasing, particularly when compared to industrialized economies. Microfinance, despite its modest scope, is essential to the uplift of certain communities in the area. It is remarkable for its focus on entrepreneurship and inclusivity, to bridge wealth disparities and raise upward mobility through assistance for small enterprises and the advancement of financial inclusion. The microfinance environment in North America has changed recently. As key stakeholders, Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFIs) provide loans and financial services to marginalized populations. Peer-to-peer micro lending has also been made easier by the emergence of Internet lending services like Kiva, which link borrowers and lenders both locally and globally. The United States dominates North American microfinance, with a larger sector than Canada. Numerous reasons contribute to its strength, such as the country's bigger population and the variety of localities facing varied degrees of financial need. Through programs like the CDFI Fund, which has invested over $5 billion into Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFIs) since 1994, the US has shown a significant commitment to microfinance. CDFIs support a variety of projects, from small businesses to affordable housing and community development. Also, the Association for Enterprise Opportunity (AEO) reports that microloans in the US, which have an average value of $13,100, have greatly boosted entrepreneurship, with 88% of clients using the money to launch or grow their enterprises. Additionally, government support through Small Business Administration (SBA) programs further supports microfinance efforts, underscoring the United States' leading role in fostering financial inclusion and economic empowerment within the region. Microfinance Market Competitive Landscape The microfinance industry has seen a notable upsurge in creative methods in recent years. A significant focus on mobile-based financial services was evident in 2023 with the release of new apps and digital platforms designed specifically with microfinance clients in mind. In 2022, MFIs and tech companies began to collaborate more frequently on fintech projects to increase operational effectiveness and reach unbanked customers. In 2021, new customized microloan products were launched to cater to certain demands including financing for schooling or climate-resilient agriculture. It indicates that the microfinance industry is always striving to be more flexible and customized. Increased rivalry among microfinance firms encourages efficiency, creativity, and cost savings for financial goods. Because of the increased competition and creative approaches used to target underprivileged people, this competitive landscape encourages more financial inclusion and outreach. Also, the growth of a varied range of market participants leads to a variety of microfinance products designed to fulfill particular requirements and financial goals. Market saturation, on the other hand, carries a possible risk of driving unsustainable practices and riskier lending because of fierce competition. Because regulators need to keep a close eye on the market to reduce risks and guarantee the integrity and sustainability of microfinance operations.Microfinance Market Scope: Inquire Before Buying
Global Microfinance Market Report Coverage Details Base Year: 2023 Forecast Period: 2024-2030 Historical Data: 2018 to 2023 Market Size in 2023: US $ 185.85 Bn. Forecast Period 2024 to 2030 CAGR: 12.5% Market Size in 2030: US $ 423.87 Bn. Segments Covered: by Service Type Group And Individual Micro Credit Leasing Micro Investment Funds Insurance Savings And Checking Accounts by Providers Banks Non-banks Microfinance Market, by Region
North America (United States, Canada and Mexico) Europe (UK, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Sweden, Austria and Rest of Europe) Asia Pacific (China, South Korea, Japan, India, Australia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam, Taiwan, Bangladesh, Pakistan and Rest of APAC) Middle East and Africa (South Africa, GCC, Egypt, Nigeria and Rest of ME&A) South America (Brazil, Argentina Rest of South America)Key Players in the Microfinance Market
1. Asiasociety 2. eco-business 3. Bandhan Bank 4. BRAC 5. Grameen Bank 6. Banco Compartamos 7. Kiva 8. e-mfp 9. European investment bank 10. EIF 11. Reserved Bank of India 12. Oliverwyman 13. Gojo & Company 14. greenfinanceplatform 15. LendingClub 16. prosper marketplace 17. PayActiv 18. Oportun 19. Upstart 20. Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd. 21. Pacific Community Ventures 22. PT Bank Rakyat Indonesia Persero Tbk FAQs: 1. What are the main products and services offered by MFIs? Ans. MFIs offer a range of financial products and services, including microloans for business expansion or income-generating activities, savings accounts, microinsurance, and money transfer services. 2. What are the challenges facing the Microfinance market? Ans. Challenges in the microfinance sector include sustainability concerns, over-indebtedness among clients, regulatory constraints, and limited access to funding, risk management issues, and the need for continuous innovation to meet evolving client needs. 3. What is the projected market size & and growth rate of the Microfinance Market? Ans. The Microfinance Market size was valued at USD 185.85 Billion in 2023 and the total Microfinance revenue is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.5% from 2023 to 2030, reaching nearly USD 423.87 Billion in 2030. 4. What segments are covered in the Microfinance Market report? Ans. The segments covered in the Microfinance market report are type and Provider.
1. Microfinance Market Introduction 1.1. Study Assumption and Market Definition 1.2. Scope of the Study 1.3. Executive Summary 2. Microfinance Market: Dynamics 2.1. Microfinance Market Trends by Region 2.1.1. North America Microfinance Market Trends 2.1.2. Europe Microfinance Market Trends 2.1.3. Asia Pacific Microfinance Market Trends 2.1.4. Middle East and Africa Microfinance Market Trends 2.1.5. South America Microfinance Market Trends 2.2. Microfinance Market Dynamics by Region 2.2.1. North America 2.2.1.1. North America Microfinance Market Drivers 2.2.1.2. North America Microfinance Market Restraints 2.2.1.3. North America Microfinance Market Opportunities 2.2.1.4. North America Microfinance Market Challenges 2.2.2. Europe 2.2.2.1. Europe Microfinance Market Drivers 2.2.2.2. Europe Microfinance Market Restraints 2.2.2.3. Europe Microfinance Market Opportunities 2.2.2.4. Europe Microfinance Market Challenges 2.2.3. Asia Pacific 2.2.3.1. Asia Pacific Microfinance Market Drivers 2.2.3.2. Asia Pacific Microfinance Market Restraints 2.2.3.3. Asia Pacific Microfinance Market Opportunities 2.2.3.4. Asia Pacific Microfinance Market Challenges 2.2.4. Middle East and Africa 2.2.4.1. Middle East and Africa Microfinance Market Drivers 2.2.4.2. Middle East and Africa Microfinance Market Restraints 2.2.4.3. Middle East and Africa Microfinance Market Opportunities 2.2.4.4. Middle East and Africa Microfinance Market Challenges 2.2.5. South America 2.2.5.1. South America Microfinance Market Drivers 2.2.5.2. South America Microfinance Market Restraints 2.2.5.3. South America Microfinance Market Opportunities 2.2.5.4. South America Microfinance Market Challenges 2.3. PORTER’s Five Forces Analysis 2.4. PESTLE Analysis 2.5. Technology Roadmap 2.6. Regulatory Landscape by Region 2.6.1. North America 2.6.2. Europe 2.6.3. Asia Pacific 2.6.4. Middle East and Africa 2.6.5. South America 2.7. Key Opinion Leader Analysis For Microfinance Industry 2.8. Analysis of Government Schemes and Initiatives For Microfinance Industry 2.9. Microfinance Market Trade Analysis 2.10. The Global Pandemic Impact on Microfinance Market 3. Microfinance Market: Global Market Size and Forecast by Segmentation by Demand and Supply Side (by Value in USD Million) 2023-2030 3.1. Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 3.1.1. Group And Individual Micro Credit 3.1.2. Leasing 3.1.3. Micro Investment Funds 3.1.4. Insurance 3.1.5. Savings And Checking Accounts 3.2. Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 3.2.1. Banks 3.2.2. Non-banks 3.3. Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Region (2023-2030) 3.3.1. North America 3.3.2. Europe 3.3.3. Asia Pacific 3.3.4. Middle East and Africa 3.3.5. South America 4. North America Microfinance Market Size and Forecast by Segmentation (by Value in USD Million) 2023-2030 4.1. North America Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 4.1.1. Group And Individual Micro Credit 4.1.2. Leasing 4.1.3. Micro Investment Funds 4.1.4. Insurance 4.1.5. Savings And Checking Accounts 4.2. North America Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 4.2.1. Banks 4.2.2. Non-banks 4.3. North America Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Country (2023-2030) 4.3.1. United States 4.3.1.1. United States Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 4.3.1.1.1. Group And Individual Micro Credit 4.3.1.1.2. Leasing 4.3.1.1.3. Micro Investment Funds 4.3.1.1.4. Insurance 4.3.1.1.5. Savings And Checking Accounts 4.3.1.2. United States Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 4.3.1.2.1. Banks 4.3.1.2.2. Non-banks 4.3.2. Canada 4.3.2.1. Canada Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 4.3.2.1.1. Group And Individual Micro Credit 4.3.2.1.2. Leasing 4.3.2.1.3. Micro Investment Funds 4.3.2.1.4. Insurance 4.3.2.1.5. Savings And Checking Accounts 4.3.2.2. Canada Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 4.3.2.2.1. Banks 4.3.2.2.2. Non-banks 4.3.3. Mexico 4.3.3.1. Mexico Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 4.3.3.1.1. Group And Individual Micro Credit 4.3.3.1.2. Leasing 4.3.3.1.3. Micro Investment Funds 4.3.3.1.4. Insurance 4.3.3.1.5. Savings And Checking Accounts 4.3.3.2. Mexico Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 4.3.3.2.1. Banks 4.3.3.2.2. Non-banks 5. Europe Microfinance Market Size and Forecast by Segmentation (by Value in USD Million) 2023-2030 5.1. Europe Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 5.2. Europe Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 5.3. Europe Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Country (2023-2030) 5.3.1. United Kingdom 5.3.1.1. United Kingdom Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 5.3.1.2. United Kingdom Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 5.3.2. France 5.3.2.1. France Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 5.3.2.2. France Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 5.3.3. Germany 5.3.3.1. Germany Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 5.3.3.2. Germany Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 5.3.4. Italy 5.3.4.1. Italy Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 5.3.4.2. Italy Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 5.3.5. Spain 5.3.5.1. Spain Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 5.3.5.2. Spain Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 5.3.6. Sweden 5.3.6.1. Sweden Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 5.3.6.2. Sweden Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 5.3.7. Austria 5.3.7.1. Austria Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 5.3.7.2. Austria Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 5.3.8. Rest of Europe 5.3.8.1. Rest of Europe Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 5.3.8.2. Rest of Europe Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 6. Asia Pacific Microfinance Market Size and Forecast by Segmentation (by Value in USD Million) 2023-2030 6.1. Asia Pacific Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 6.2. Asia Pacific Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 6.3. Asia Pacific Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Country (2023-2030) 6.3.1. China 6.3.1.1. China Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 6.3.1.2. China Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 6.3.2. S Korea 6.3.2.1. S Korea Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 6.3.2.2. S Korea Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 6.3.3. Japan 6.3.3.1. Japan Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 6.3.3.2. Japan Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 6.3.4. India 6.3.4.1. India Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 6.3.4.2. India Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 6.3.5. Australia 6.3.5.1. Australia Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 6.3.5.2. Australia Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 6.3.6. Indonesia 6.3.6.1. Indonesia Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 6.3.6.2. Indonesia Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 6.3.7. Malaysia 6.3.7.1. Malaysia Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 6.3.7.2. Malaysia Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 6.3.8. Vietnam 6.3.8.1. Vietnam Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 6.3.8.2. Vietnam Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 6.3.9. Taiwan 6.3.9.1. Taiwan Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 6.3.9.2. Taiwan Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 6.3.10. Rest of Asia Pacific 6.3.10.1. Rest of Asia Pacific Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 6.3.10.2. Rest of Asia Pacific Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 7. Middle East and Africa Microfinance Market Size and Forecast by Segmentation (by Value in USD Million) 2023-2030 7.1. Middle East and Africa Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 7.2. Middle East and Africa Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 7.3. Middle East and Africa Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Country (2023-2030) 7.3.1. South Africa 7.3.1.1. South Africa Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 7.3.1.2. South Africa Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 7.3.2. GCC 7.3.2.1. GCC Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 7.3.2.2. GCC Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 7.3.3. Nigeria 7.3.3.1. Nigeria Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 7.3.3.2. Nigeria Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 7.3.4. Rest of ME&A 7.3.4.1. Rest of ME&A Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 7.3.4.2. Rest of ME&A Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 8. South America Microfinance Market Size and Forecast by Segmentation (by Value in USD Million) 2023-2030 8.1. South America Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 8.2. South America Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 8.3. South America Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Country (2023-2030) 8.3.1. Brazil 8.3.1.1. Brazil Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 8.3.1.2. Brazil Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 8.3.2. Argentina 8.3.2.1. Argentina Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 8.3.2.2. Argentina Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 8.3.3. Rest Of South America 8.3.3.1. Rest Of South America Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Service Type (2023-2030) 8.3.3.2. Rest Of South America Microfinance Market Size and Forecast, by Providers (2023-2030) 9. Global Microfinance Market: Competitive Landscape 9.1. MMR Competition Matrix 9.2. Competitive Landscape 9.3. Key Players Benchmarking 9.3.1. Company Name 9.3.2. Business Segment 9.3.3. End-user Segment 9.3.4. Revenue (2022) 9.3.5. Company Locations 9.4. Leading Microfinance Market Companies, by market capitalization 9.5. Market Structure 9.5.1. Market Leaders 9.5.2. Market Followers 9.5.3. Emerging Players 9.6. Mergers and Acquisitions Details 10. Company Profile: Key Players 10.1. Asiasociety 10.1.1. Company Overview 10.1.2. Business Portfolio 10.1.3. Financial Overview 10.1.4. SWOT Analysis 10.1.5. Strategic Analysis 10.1.6. Scale of Operation (small, medium, and large) 10.1.7. Details on Partnership 10.1.8. Regulatory Accreditations and Certifications Received by Them 10.1.9. Awards Received by the Firm 10.1.10. Recent Developments 10.2. eco-business 10.3. Bandhan Bank 10.4. BRAC 10.5. Grameen Bank 10.6. Banco Compartamos 10.7. Kiva 10.8. e-mfp 10.9. European investment bank 10.10. EIF 10.11. Reserved Bank of India 10.12. Oliverwyman 10.13. Gojo & Company 10.14. greenfinanceplatform 10.15. LendingClub 10.16. prosper marketplace 10.17. PayActiv 10.18. Oportun 10.19. Upstart 10.20. Kotak Mahindra Bank Ltd. 10.21. Pacific Community Ventures 10.22. PT Bank Rakyat Indonesia Persero Tbk 11. Key Findings 12. Industry Recommendations 13. Microfinance Market: Research Methodology 14. Terms and Glossary